
Unlocking the Mystery of Watts and Volts: How Many Volts is 1200 Watts?
Mar 17, 2025 · To calculate the voltage, we need to know the amperage. Let''s assume we''re working with a standard household circuit with an amperage of 10 amps. Using the formula:

Unlocking the Mystery of Watts and Volts: How Many Volts is 1200 Watts?
Mar 17, 2025 · When it comes to understanding electricity, two of the most fundamental concepts are watts and volts. While they are closely related, they measure different aspects of electrical

Watts To Volts Converter (W to V): Calculator + Conversion
2 days ago · To calculate volts from watts, we need to rearrange this formula by expressing voltage like this: Volt = Watts / Amps. To convert watts to volts, we need to know how many

Watts to Watt-Hours: Calculator for Power Stations and Solar
Nov 18, 2023 · This blog post delves into the essentials of watts to watt-hour conversion. We provide a handy watts to watt-hour calculator and how to apply that information when choosing
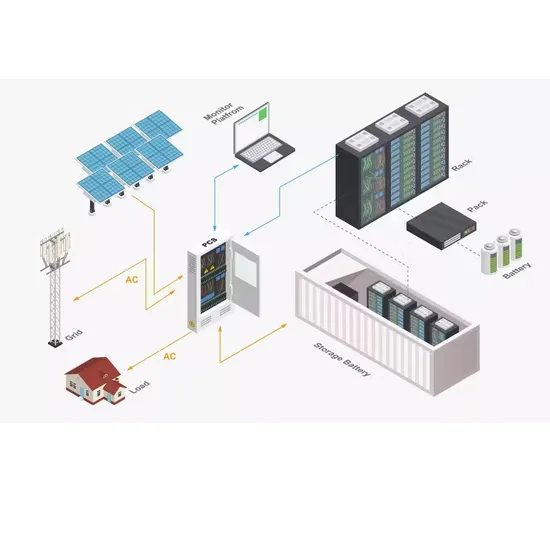
6 FAQs about [How many watts is a 1200w solar light equivalent to 220 volts]
How many watts are in a volt?
If you have a 1 amp circuit, 1 volt is equal to 1 watt. If you have a 100 amp circuit, 1 volt is equal to 100 watts. Example 2: How many watts in a volt? Amps are the key here as well; in a 1 amp circuit, you have 1 watt per volt. If you have a 10 amp circuit, you will have 10 watts in a volt.
How many volts in 1300 watts?
For an AC circuit, the voltage V in volts is equal to the real power P in watts divided by the product of the current I in amps and the power factor. For example, let’s convert 1,300 watts to voltage for an AC electrical circuit with 12 amps of current and a power factor of 0.9. In this example, 1,300 watts is equal to 120.4 volts at 12 amps.
How to convert watts to volts?
If we know the amperage (A), we can easily convert watts to volts. For the W to V conversion, we can use the formula for electric power: P (W) = I (A) * V (V) To calculate volts from watts, we need to rearrange this formula by expressing voltage like this: Volt = Watts / Amps
How to calculate solar panel wattage?
Also Check: – Hand Drying Footprint Calculator Calculating solar panel wattage involves a series of methodical steps: Determine the panel specifications: Locate the Vmp and Imp values, which are typically provided on the panel’s datasheet. Apply the formula: Multiply Vmp by Imp to derive the maximum power output in watts.
How much power does a 400W solar panel produce?
Optimal conditions: On a clear, sunny day, with the panel perfectly oriented towards the sun, a 400W panel might generate output close to its rated capacity. Typical conditions: Under average conditions, accounting for various influencing factors, you might expect an output between 320 to 360 watts during peak sunlight hours.
What is the difference between volts and Watts?
Volts (V): A unit of electric potential and electromotive force. It's the driving force that pushes the current through a circuit. Watts (W): A unit of power representing the rate of energy per unit time. It indicates how much energy an appliance uses or a circuit transmits. Conversion Formulas DC Volts to Watts:
Random Links
- Genuine manufacturer inverter brand
- Light energy storage battery control
- Photovoltaic glass and new energy
- Myanmar complete photovoltaic solar system
- Factory price 3 phase breaker in indonesia
- Nicosia Electricity Company Energy Base Station
- Promote the improvement of new energy storage mechanism
- Is there solar air conditioning in Havana
- Marshall Islands communication base station inverter grid connection project cost
- Democratic Republic of Congo Home Inverter Purchase
- Indonesia Surabaya RV Energy Storage Battery
- Are the power distribution cabinet and battery cabinet big
- Lilongwe Photovoltaic Power Station Energy Storage Design
- Can the inverter use 24v
- Energy storage battery pump
- 400W Folding Solar
- Best hybrid inverter 15kw in China for sale
- Hot sale 50kw sunsynk inverter factory supplier
- Can lithium battery packs with the same voltage and capacity be connected in parallel
- Wholesale 10000 watt inverter in Pakistan
- Fiji uninterruptible power supply model differences
- Peak-valley energy storage system
- Container generator room grounding
Residential Solar Storage & Inverter Market Growth
The global residential solar storage and inverter market is experiencing rapid expansion, with demand increasing by over 300% in the past three years. Home energy storage solutions now account for approximately 35% of all new residential solar installations worldwide. North America leads with 38% market share, driven by homeowner energy independence goals and federal tax credits that reduce total system costs by 26-30%. Europe follows with 32% market share, where standardized home storage designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting residential storage for backup power and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 4-7 years. Modern home installations now feature integrated systems with 10-30kWh capacity at costs below $700/kWh for complete residential energy solutions.
Home Solar System Innovations & Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving home solar storage and inverter performance while reducing costs. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 40% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 15+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,200/kW to $650/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow home systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing homeowner savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for solar storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $600/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have improved ROI significantly, with residential projects typically achieving payback in 5-8 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard home systems (5-10kWh) starting at $8,000 and premium systems (15-20kWh) from $12,000, with financing options available for homeowners.
