
How much power does an Inverter use just sitting there idling?
Oct 30, 2020 · Thanks in advance. P.S. - Ultimately, I''d also like to have an automatic switch that would switch to AC if the battery dropped to a preset level AND turned the inverter off (if it is

How to Choose the Right Inverter for Lithium Batteries?
Apr 11, 2025 · Answer: To choose the right inverter for lithium batteries, match the inverter''s voltage and capacity to your battery''s specifications, prioritize pure sine wave inverters for

Understanding Inverter Power Consumption: Do Inverters Use Power
Mar 12, 2025 · In today''s energy-conscious world, many homeowners and businesses are increasingly turning to energy-efficient solutions, and inverters have become an essential part

How Long Will a Battery Last with an Inverter? Calculate Your Power
Mar 13, 2025 · An inverter battery lasts about 5 to 10 hours when fully charged. The backup time depends on the battery capacity and the load, which is the total energy consumption. You can

How to calculate actual power consumption off of a battery through inverter
May 3, 2024 · Once you have HWinfo or some similar tool that can check power draw, you can get a rough idea of how much power you ACTUALLY use for a given period of time. That is

Inverter Power Draw: How Much Power Does An Inverter Use From A Battery
Mar 17, 2025 · Understanding inverter power draw is crucial for efficiently managing battery usage and ensuring longer operational life. As we explore this topic further, we will discuss how to

Inverter Efficiency: Understanding How Much Power You''re
Jul 21, 2025 · In simple terms, inverter efficiency refers to how well an inverter converts DC electricity into usable AC power. No inverter is 100% efficient—some energy always gets lost

Inverter Usage Calculator & Formula Online Calculator Ultra
Oct 3, 2024 · If an inverter has a power rating of 1000 watts and is used for 4 hours daily, with a battery efficiency of 85%, the energy consumption can be calculated as: [ text {Daily Energy

How Long Will A Battery Last Using An Inverter? Calculate
Mar 27, 2025 · A 12-volt, 100Ah battery can power a 1000-watt inverter load for about 1.08 hours. This estimate includes an inverter efficiency of 90%. Use this formula for quick calculations:
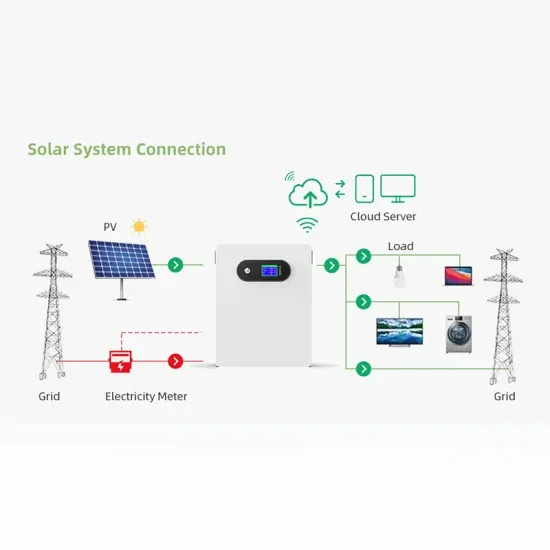
6 FAQs about [Power consumption with inverter battery]
How much power does an inverter use?
But this amount may vary depending on the type of battery bank used and the types of loads connected to the inverter. Typically, in a no-load current, the energy drawn by the inverter is only 2 to 10 watts an hour. What Amount of Power is Wasted by Inverter? Do not confuse the inverter’s no-load current with the efficiency rating of the inverter.
Do inverters drain batteries?
Yes, inverters drain batteries if not in use and the amount of power drained depends on the design and size of the inverter. Generally, it is said that modern inverters save more power than traditional ones. And if an inverter is left connected to the batteries without any load, then it will drain the battery completely over time.
What is a battery inverter?
An inverter is an electronic device that converts direct current (DC) from batteries or renewable sources like solar panels into alternating current (AC) for use in household appliances. Why is battery efficiency important? Battery efficiency indicates how much of the stored energy can be effectively used.
Why does an inverter consume a lot of power?
This may sound confusing because at times when the inverter is not connected to any load then also it consumes power. It is because inverters produce waveforms even on standby mode and the larger the inverter is the more power it needs to start.
How much power does an inverter use in idle mode?
Remember, the higher the voltage is the greater the no-load current will be. In some configurations, a standard inverter may consume between 0.416 amps and 2.83 amps of power in idle mode. But this amount may vary depending on the type of battery bank used and the types of loads connected to the inverter.
Does an inverter draw power when not in use?
So, if the inverter is on the power consumed by it from the no-load current cannot be avoided. However, it can become negligible if connected to a large load. Suppose you are using a 5000 watts inverter and run it at almost full load then 0.4 no-load currents can be ignored. Now, let’s see does an inverter draw power when not in use.
Random Links
- Manila Telecommunication Base Station Lead-acid Battery Tower
- The nearest communication base station flywheel energy storage environmentally friendly electricity
- Base station distribution box bidding
- Photovoltaic 30 kWh energy storage battery
- Mobile safe voltage power supply box
- Nassau High Voltage Inverter
- Greek battery energy storage cabinet manufacturer
- Smart PV combiner box price
- Cambodia distributed energy storage system battery
- Manila power supply side industrial and commercial energy storage system
- Solar cell wattage and conversion rate
- Best 2000w solar inverter in China Seller
- 2000w solar inverter for sale in Laos
- China backup inverter systems in Belgium
- Solar base station flywheel energy storage equipment manufacturers
- Double glass light transmission component parameters
- Koten safety breaker factory in Pakistan
- Uruguay Energy Storage System Agent
- Mechanical energy storage device coil spring
- Precautions for installing battery cabinet
- Battery storage power
- Wind power solar energy storage
- The EMS brand of communication base stations used in Bucharest
Residential Solar Storage & Inverter Market Growth
The global residential solar storage and inverter market is experiencing rapid expansion, with demand increasing by over 300% in the past three years. Home energy storage solutions now account for approximately 35% of all new residential solar installations worldwide. North America leads with 38% market share, driven by homeowner energy independence goals and federal tax credits that reduce total system costs by 26-30%. Europe follows with 32% market share, where standardized home storage designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting residential storage for backup power and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 4-7 years. Modern home installations now feature integrated systems with 10-30kWh capacity at costs below $700/kWh for complete residential energy solutions.
Home Solar System Innovations & Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving home solar storage and inverter performance while reducing costs. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 40% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 15+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,200/kW to $650/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow home systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing homeowner savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for solar storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $600/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have improved ROI significantly, with residential projects typically achieving payback in 5-8 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard home systems (5-10kWh) starting at $8,000 and premium systems (15-20kWh) from $12,000, with financing options available for homeowners.
