
Control and filter design of three-phase inverters for
Aug 18, 2025 · Abstract— The trend toward using inverters in distributed generation systems and micro-grids has raised the importance of achieving low-distortion, high-quality power export

A review on single-phase boost inverter technology for low power grid
Feb 1, 2024 · Solar Photovoltaic (SPV) inverters have made significant advancements across multiple domains, including the booming area of research in single-stage boosting inverter
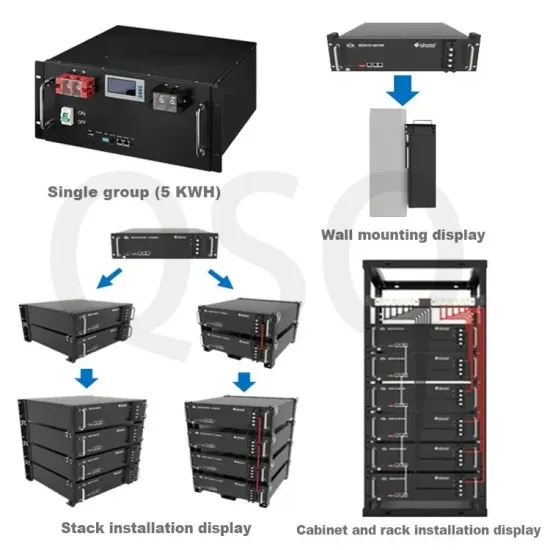
High-voltage VS Low-voltage Inverters: What''s the difference?
May 14, 2025 · Confused about high-voltage vs low-voltage inverters? This easy-to-read guide explains the differences, pros, cons, and real-world uses—perfect for anyone exploring solar

Is there a difference between a high voltage inverter and a low voltage
Jan 5, 2024 · The choice between low-voltage and high-voltage hybrid inverters depends on system size, power requirements, and availability and investment opportunities. Low voltage is

Three-phase photovoltaic inverter control strategy for low voltage grid
Dec 1, 2023 · The inverter control measures two-line voltages at the point of connection to the grid, the DC link voltage, and two inverter output currents. These measurements are the

On Grid Inverter: Basics, Working Principle and Function
Jun 30, 2022 · A grid-tie inverter (GTI for short) also called on-grid inverter, which is a special inverter. In addition to converting direct current into alternating current, the output alternating

Grid Interconnection of PV System Based on Interleaved
Mar 8, 2022 · In this paper, a PV system for grid connection is proposed. PV produces low voltage dc output but grid interconnection of this system requires power converters to meet the grid
Consistency control of grid-connected substation voltage
Jul 16, 2025 · By analyzing the impact of exceeding voltage limits after the photovoltaic grid connection, this method ensures effective voltage regulation in the grid-connected substation

6 FAQs about [Inverter high voltage and low voltage grid connection]
What is a high voltage grid connected inverter?
The high-voltage grid-connected inverter has a high-voltage output capacity. The AC grid-connected voltage levels of 1100V DC high-voltage inverters are generally 480Vac, 500Vac, 540Vac, etc., and the AC grid-connected voltage level of 1500V DC high-voltage inverters is 800Vac.
What is a high-voltage grid connection?
Next, we will explain in detail the differences between these two grid connection methods. High-voltage grid connection usually refers to directly connecting a photovoltaic power station to a medium-high voltage power grid. Its voltage level is generally above 10 kilovolts. Common voltage levels include 10 kV, 35 kV, etc.
What is the difference between high voltage and low voltage grid connection?
The high-voltage grid connection mode is more suitable for large-scale ground photovoltaic power stations that require long-distance transmission, while the low-voltage grid connection is more suitable for small-scale, short-distance transmission distributed projects.
What is the voltage level of a low-voltage grid connection system?
The voltage level of the low-voltage grid connection system accessing the power grid is usually 380V (three-phase) or 220V (single-phase), which is exactly the common voltage in our daily electricity consumption.
Why should you choose a low-voltage grid connection system?
The low-voltage grid connection system does not require complex power transmission equipment, and installation and maintenance are also more convenient. For residents and small industrial and commercial users, the low-voltage grid connection system is undoubtedly a more economical and practical choice.
What is the control design of a grid connected inverter?
The control design of this type of inverter may be challenging as several algorithms are required to run the inverter. This reference design uses the C2000 microcontroller (MCU) family of devices to implement control of a grid connected inverter with output current control.
Random Links
- Quad circuit breaker in China in Auckland
- 1000 tier energy storage system price
- Home energy storage bms
- European outdoor energy storage battery manufacturers
- Zhongya Photovoltaic Energy Storage System Energy Storage Lithium Battery
- Can electrochemical energy storage power stations be built in cities
- Is Colombian microinverter good
- 7 5v uninterruptible power supply
- 30w solar street light
- 5g base station explosion-proof lithium battery
- Stacking Outdoor Power Supply
- Usb c power station for sale in Ukraine
- Hungary Pecs energy storage battery cycle life
- Safety precautions for energy storage power stations
- Grid Energy Storage Standards
- Guatemala Solar PV Inverter
- Super Nano Capacitor Battery
- How to charge the battery pack in the battery cabinet
- Factory price furnace breaker in Moldova
- How many energy storage equipment manufacturers are there in St Johns
- Communication green base station bottom plate
- Factory price main switchgear in Chicago
- North Asia Energy Storage Battery Order
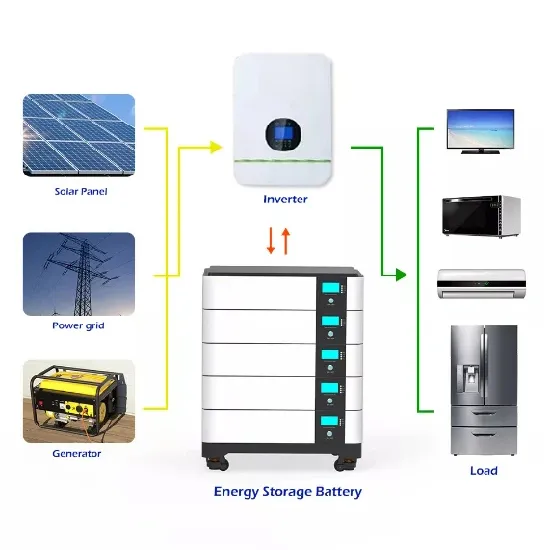
Residential Solar Storage & Inverter Market Growth
The global residential solar storage and inverter market is experiencing rapid expansion, with demand increasing by over 300% in the past three years. Home energy storage solutions now account for approximately 35% of all new residential solar installations worldwide. North America leads with 38% market share, driven by homeowner energy independence goals and federal tax credits that reduce total system costs by 26-30%. Europe follows with 32% market share, where standardized home storage designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting residential storage for backup power and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 4-7 years. Modern home installations now feature integrated systems with 10-30kWh capacity at costs below $700/kWh for complete residential energy solutions.
Home Solar System Innovations & Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving home solar storage and inverter performance while reducing costs. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 40% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 15+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,200/kW to $650/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow home systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing homeowner savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for solar storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $600/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have improved ROI significantly, with residential projects typically achieving payback in 5-8 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard home systems (5-10kWh) starting at $8,000 and premium systems (15-20kWh) from $12,000, with financing options available for homeowners.
