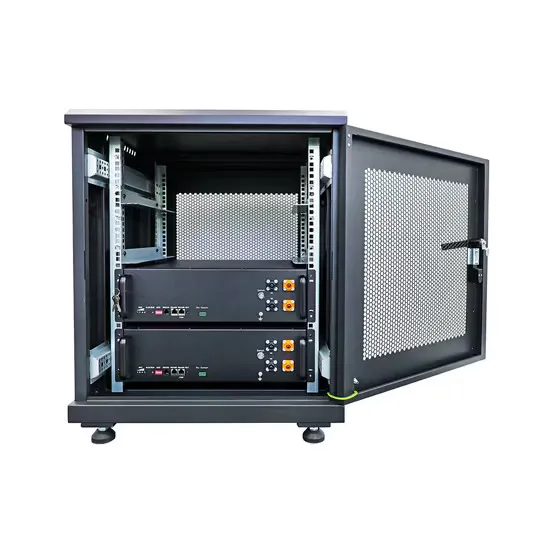

Operation and control of uninterruptible power supply system
Jan 1, 2024 · An uninterruptible power supply (UPS) is an electrical apparatus that provides a continuous, stable, and uninterrupted supply of power to critical loads. UPSs can supply power

Smart UPS 1kva 10kva Wide Voltage Input Range Uninterruptible Power
1. Tower and rack installation modes can be switched arbitrarily, convenient for users to choose 2. Digital control, the control system is more stable and reliable 3. Wide voltage input range,
Sunlooker 6KVA 10KVA Tower &Rack Mount Uninterruptible Power Supply
1. Tower and rack installation modes can be switched arbitrarily, convenient for users to choose 2. Digital control, the control system is more stable and reliable 3. Wide voltage input range,
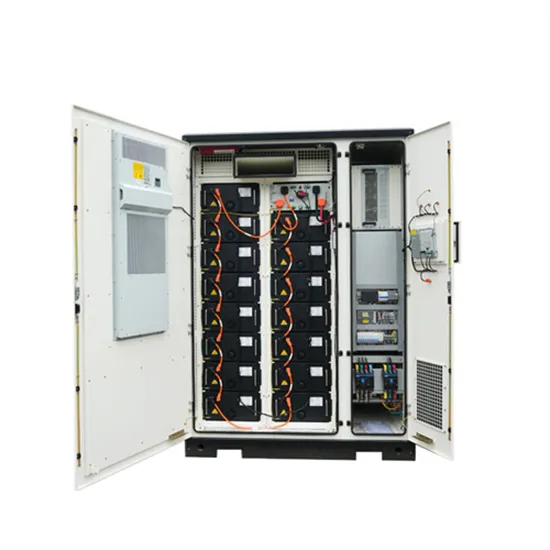

Enabling uninterrupted power: Design for reliability in
Feb 13, 2025 · Enabling uninterrupted power: Design for reliability in UPS systems itate and verify consistent performance of uninterruptible power supply (UPS) systems. Planning and

6 FAQs about [Uninterruptible power supply full load output characteristics]
What is a uninterruptible power supply (UPS)?
A UPS, or a uninterruptible power supply, is a device used to backup a power supply to prevent devices and systems from power supply problems, such as a power failure or lightning strikes.
What are the different types of uninterruptible power supplies?
There are two main categories of uninterruptible power supplies (UPSs) 1, static and rotary. As the name implies, static UPSs do not have any moving parts in their con-verters. Whereas, rotary UPS use mechanical parts that rotate, such as motor/gen-erators, to function. This paper focuses only on static UPSs.
What is a rotary uninterruptible power system?
A UPS is normally referred to as an uninterruptible power supply, but it’s also known as uninterruptible power system. Note that rotary UPS are covered in IEC 88528-11:2004 Reciprocating internal combustion engine driven alternating current generating sets - Part 11: Rotary uninterruptible power systems - Perfor-mance requirements and test methods.
What is a ups & how does it work?
A UPS, or a uninterruptible power supply, is a device used to backup a power supply to prevent devices and systems from power supply problems, such as a power failure or lightning strikes. A UPS can help prevent power supply problems that can often occur on a production site, such as an instantaneous voltage drop and a power failure.
Do uninterruptible power supply systems provide protection?
"Uninterruptible power supply systems provide protection." IEEE Industrial Electronics Magazine 1, no. 1 (2007): 28-38. . Rahmat, M., S. Jovanovic, and K. L. Lo. "Reliability and availability modelling of uninterruptible power supply systems using Monte-Carlo simulation."
What is the minimum power factor for UPS?
According to the IEEE standard ANSI/IEEE 446–1987, minimum power factor is 0.8 at the rated load and harmonics content less than 5% is preferred for the input rectifier of the UPS system. Table 8. Typical 3-Ø UPS System Specification by ANSI/IEEE 446–1987 . Fig. 27. Input Voltage and Current waveform.
Random Links
- The inverter outputs high voltage
- Tajikistan EK Power Storage System
- What is the size of the photovoltaic panels on the roof of West Asia
- Which energy storage module equipment is best in Tajikistan
- Lithium iron phosphate power lithium battery pack
- Wholesale 500w solar inverter in Angola
- Polycrystalline 260w photovoltaic panel price
- What types of energy storage battery products are there
- Can I install photovoltaic power without a combiner box
- Power supply for communication base stations Wind power supply
- 16a Battery cabinet size
- Lithium battery pack notice
- 240v circuit breaker in China in Poland
- Myanmar energy storage battery supporting manufacturers
- Nicaragua Large Uninterruptible Power Supply Manufacturer
- Bangji high frequency inverter installation
- Home 200w inverter
- Usb c power station for sale in Honduras
- Communication base station China solar photovoltaic panels
- Luanda RV Energy Storage Battery
- Tunisia good lithium battery pack factory price
- Home Flow Battery
- Liechtenstein Photovoltaic Cell Photovoltaic Site
Residential Solar Storage & Inverter Market Growth
The global residential solar storage and inverter market is experiencing rapid expansion, with demand increasing by over 300% in the past three years. Home energy storage solutions now account for approximately 35% of all new residential solar installations worldwide. North America leads with 38% market share, driven by homeowner energy independence goals and federal tax credits that reduce total system costs by 26-30%. Europe follows with 32% market share, where standardized home storage designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting residential storage for backup power and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 4-7 years. Modern home installations now feature integrated systems with 10-30kWh capacity at costs below $700/kWh for complete residential energy solutions.
Home Solar System Innovations & Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving home solar storage and inverter performance while reducing costs. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 40% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 15+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,200/kW to $650/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow home systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing homeowner savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for solar storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $600/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have improved ROI significantly, with residential projects typically achieving payback in 5-8 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard home systems (5-10kWh) starting at $8,000 and premium systems (15-20kWh) from $12,000, with financing options available for homeowners.
