
Two-stage three-phase photovoltaic grid-connected inverter control
Jun 1, 2025 · In this article, a novel control method of the grid-connected inverter (GCI) based on the off-policy integral reinforcement learning (IRL) method is presented to solve two-stage

Sliding Mode Control of Grid-connected Inverters Using
Sep 30, 2023 · Abstract—In this paper, the switching command is produced by a sliding mode controller so that inverter output current follows the load current. To this end, an appropriate

Sliding Mode Control of Grid-connected Inverters Using Inverter Output
Jun 14, 2019 · In this paper, the switching command is produced by a sliding mode controller so that inverter output current follows the load current. To this end, an appropriate sliding surface

Analysis of Output Admittance Characteristics and Grid-Connected
Jan 4, 2025 · The inverter connected to the grid employs a phase-locked loop to synchronize with the grid, and its dynamic characteristics can impact the stability of the system. Moreover, due

Stability analysis of multi-parallel inverters with different control
Apr 1, 2025 · The traditional grid-based inverter control has the disadvantage of low inertia or even no inertia, and large-scale access will reduce the inertia of the power system, so it is

A comprehensive review on inverter topologies and control strategies
Oct 1, 2018 · The requirements for the grid-connected inverter include; low total harmonic distortion of the currents injected into the grid, maximum power point tracking, high efficiency,

SoC–Based Inverter Control Strategy for Grid-Connected
Jan 23, 2025 · The successful integration of battery energy storage systems (BESSs) is crucial for enhancing the resilience and performance of microgrids (MGs) and power systems. This study

On Grid Inverter: Basics, Working Principle and Function
Jun 30, 2022 · A grid-tie inverter (GTI for short) also called on-grid inverter, which is a special inverter. In addition to converting direct current into alternating current, the output alternating
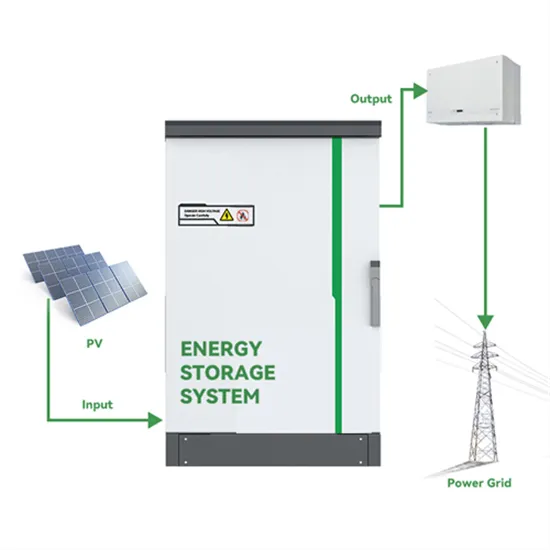
Grid-Connected, Data-Driven Inverter Control, Theory to
Jul 4, 2025 · As inverters have strict current limits, plug-and-play inverter control which proactively constrains output current is of particular interest. The industry-standard grid-connected inverter

Overview of power inverter topologies and control structures for grid
Feb 1, 2014 · In grid-connected photovoltaic systems, a key consideration in the design and operation of inverters is how to achieve high efficiency with power output for different power

6 FAQs about [Grid-connected inverter control output]
Are grid-connected inverters controlled?
Policies and ethics The control of grid-connected inverters has attracted tremendous attention from researchers in recent times. The challenges in the grid connection of inverters are greater as there are so many control requirements to be met. The different types of control techniques...
How a grid connected inverter works?
Along with that, it keeps a track on harmonics and reduces the harmonics as per grid standards (Zmood and Holmes 2003). Inverter switches play a significant part in implementing the control technique. When grid-connected inverters intentionally separate themselves from the PCC, through opening the controlled switch, they operate autonomously.
How to synchronize grid-connected inverters with grid current?
Initially, the proposed control of the grid side is introduced. Secondly, to synchronize the grid side voltage with grid current, a synchronous reference frame (SRF) based phase locked loop (PLL) is applied. Finally, the simulation of grid-connected inverters using PSIM is presented to illustrate concepts and results.
What is a grid based inverter?
In this mode, the inverter is connected to the grid at PCC and it transfers the generated power from the DC side to the AC side, i.e., grid and AC loads (Ahmed et al. 2011). The voltage reference is taken as per the grid side requirements for inverter controller.
Can a grid connected inverter be left unattended?
Do not leave the design powered when unattended. Grid connected inverters (GCI) are commonly used in applications such as photovoltaic inverters to generate a regulated AC current to feed into the grid. The control design of this type of inverter may be challenging as several algorithms are required to run the inverter.
Why is Inverter management important in grid-connected PV systems?
Proper inverter management in grid-connected PV systems ensures the stability and quality of the electricity supplied to the grid. An appropriate control strategy is necessary to ensure reliable performance over diverse system configurations and fluctuating environmental conditions.
Random Links
- Doha Battery Energy Storage System
- Islamabad Energy-saving Photovoltaic Glass Manufacturer
- Kuwait Energy Storage Battery Container Factory
- 8 yuan 21700 battery cell
- EMS construction of London communication base station
- Gaborone 12v inverter wholesale
- Photovoltaic energy storage box products
- Angola photovoltaic folding container villa wholesale
- Singapore household energy storage power supply production plant
- The role of uninterrupted power supply in base station rooms
- Outdoor power control cabinet
- DC panel battery cabinet equipment in Thailand
- Qatar cylindrical lithium battery equipment manufacturing
- Djibouti City Freight Photovoltaic Solar Onsite Energy
- Energy storage photovoltaic box substation model
- Energy storage and collection battery device
- Container base station for energy storage system
- How much energy storage should be matched with 1MW of photovoltaic power generation
- Solar portable energy storage device
- Brand new 72v inverter
- Energy storage electricity price cost
- Solar Onsite Energy Price 1000
- Kabul Energy Storage Power Sales
Residential Solar Storage & Inverter Market Growth
The global residential solar storage and inverter market is experiencing rapid expansion, with demand increasing by over 300% in the past three years. Home energy storage solutions now account for approximately 35% of all new residential solar installations worldwide. North America leads with 38% market share, driven by homeowner energy independence goals and federal tax credits that reduce total system costs by 26-30%. Europe follows with 32% market share, where standardized home storage designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting residential storage for backup power and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 4-7 years. Modern home installations now feature integrated systems with 10-30kWh capacity at costs below $700/kWh for complete residential energy solutions.
Home Solar System Innovations & Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving home solar storage and inverter performance while reducing costs. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 40% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 15+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,200/kW to $650/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow home systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing homeowner savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for solar storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $600/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have improved ROI significantly, with residential projects typically achieving payback in 5-8 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard home systems (5-10kWh) starting at $8,000 and premium systems (15-20kWh) from $12,000, with financing options available for homeowners.
