
Irregular shape battery.lithium deep cycle marine battery
Mar 20, 2023 · 1. Ultra -thin battery Ultra -thin irregular shape batteries are mainly used in micro -telephone cards, bank cards, smart cards, information cards, heating uniforms, smart shoes,

High performance shape-adjustable structural lithium-ion battery
Dec 1, 2023 · Herein, a high-performance structural lithium-ion battery composite (SLBC) is developed by encapsulating commercial-available battery core materials with hybrid fiber

Fault diagnosis and abnormality detection of lithium-ion battery
Jan 15, 2021 · However, different from other mechanical or electrical systems, lithium-ion battery packs form a quite complex system consisting of a variety of sub-systems, such as cells,

Quantitative investigation of heterogeneous lithium plating
Jun 30, 2025 · The escalation of large-format lithium-ion batteries for higher energy density counterintuitively worsens internal heterogeneity. Notably, thermal heterogeneity is a primary

Cylindrical vs. Prismatic vs. Li-Po Battery: Key Differences
Feb 29, 2024 · There are three main mainstream lithium battery packaging forms, namely cylindrical, prismatic, and lithium polymer. The three shapes of lithium batteries will eventually
Why Irregular Shape Batteries Are the Future of Wearable
Mar 18, 2025 · Irregular shape batteries offer a revolutionary solution by adapting to unique contours and forms, thereby enhancing both the functionality and comfort of wearables. This

SYNergy Deeply Works on Mini and Irregular-Shaped Lithium-ion Batteries
Jun 18, 2015 · Quite different from the standardized lithium-ion battery applications such as for mobile phones, tablets, notebooks, etc. which occupy the large share of the consumer market.

Square, Cylindrical, Soft Pack: Analysis of Manufacturing
Jun 10, 2025 · In the future, technical development routes for lithium battery packaging shapes will closely revolve around enhancing energy density, security, reducing costs, and adapting to
Comparatively Assessing different Shapes of Lithium-ion Battery
Jan 1, 2017 · Different shapes of lithium-ion batteries (LIB) are competing as energy storages for the automobile application. The shapes can be divided into cylindrical and prismatic, whereas

6 FAQs about [Irregular shape of lithium battery pack]
What are the different types of lithium battery packaging?
There are three main mainstream lithium battery packaging forms, namely cylindrical, prismatic, and lithium polymer. The three shapes of lithium batteries will eventually become cylindrical batteries, prismatic batteries and lithium polymer batteries through cylindrical winding, prismatic winding, and prismatic lamination.
What are the different shapes of lithium-ion batteries?
Pascalstrasse 8-9, 10587 Berlin, Germany Abstract Different shapes of lithium-ion batteries (LIB) are competing as energy storages for the automobile application. The shapes can be divided into cylindrical and prismatic, whereas the prismatic shape can be further divided in regard to the housing stability in Hard-Case and Pouch.
What are the different types of lithium batteries?
The three shapes of lithium batteries will eventually become cylindrical batteries, prismatic batteries and lithium polymer batteries through cylindrical winding, prismatic winding, and prismatic lamination. Different packaging structures mean different characteristics, so what are their differences? Part 1. What’s the cylindrical lithium battery?
What is a lithium polymer battery?
Lithium polymer batteries are currently the least used battery form in electric vehicles. But in fact, we are not unfamiliar with it. Most of the batteries in mobile phones are lithium polymer batteries. The biggest difference between lithium polymer, cylindrical, and prismatic batteries is that their outer casing is made of aluminum-plastic film.
What is the internal resistance of lithium polymer batteries?
Small internal resistance Lithium polymer batteries have small internal resistance. The internal resistance of lithium polymer batteries can be as low as 35Ω. Greatly reduces battery self-consumption. e.
Can lithium polymer batteries be developed based on customer needs?
Lithium battery manufacturers can also develop new battery cell models based on customer needs. However, the existing lithium polymer battery cell models are few and cannot meet market demand. At the same time, the cost of developing new models of lithium polymer batteries is relatively high.
Random Links
- Can the lead-acid battery cabinet be waterproof
- 5MWh energy storage standard container size
- How much does photovoltaic panel electricity cost in Luxembourg
- Pure sine wave inverter products
- Photovoltaic energy storage cabinet base station set
- 36kW photovoltaic grid-connected inverter
- Main circuit breaker factory in Lithuania
- 5-input 1-output photovoltaic combiner box
- How much is the Samoa battery cabinet integrated system
- European energy storage solar power generation
- Avaru Energy Storage Solar Panel Manufacturer
- Garden solar lighting large tile
- What are the main battery devices for communication base stations
- Energy storage container booster tank manufacturer ranking
- How much does a French photovoltaic curtain wall cost per square meter
- What does the new battery cabinet include
- Srp industrial energy storage
- Factory price voltage breaker in Bulgaria
- Huawei energy storage battery investment
- How big is the difference between photovoltaic panels and batteries
- Containerized generator sets for sale in Bhutan
- Factory price 3 phase breaker in Brasilia
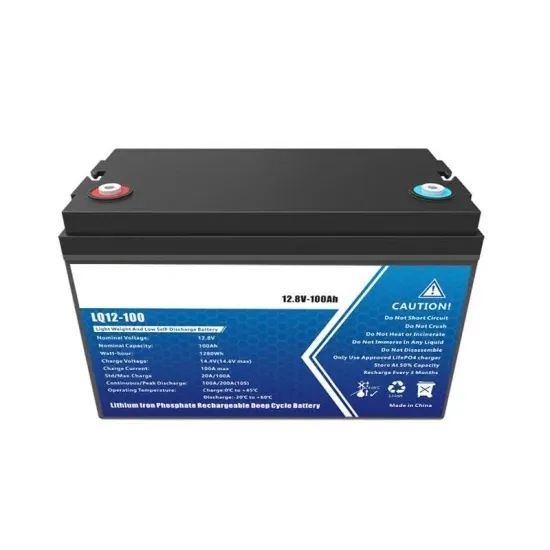
- 2 5 kWh energy storage battery
Residential Solar Storage & Inverter Market Growth
The global residential solar storage and inverter market is experiencing rapid expansion, with demand increasing by over 300% in the past three years. Home energy storage solutions now account for approximately 35% of all new residential solar installations worldwide. North America leads with 38% market share, driven by homeowner energy independence goals and federal tax credits that reduce total system costs by 26-30%. Europe follows with 32% market share, where standardized home storage designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting residential storage for backup power and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 4-7 years. Modern home installations now feature integrated systems with 10-30kWh capacity at costs below $700/kWh for complete residential energy solutions.
Home Solar System Innovations & Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving home solar storage and inverter performance while reducing costs. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 40% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 15+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,200/kW to $650/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow home systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing homeowner savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for solar storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $600/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have improved ROI significantly, with residential projects typically achieving payback in 5-8 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard home systems (5-10kWh) starting at $8,000 and premium systems (15-20kWh) from $12,000, with financing options available for homeowners.
