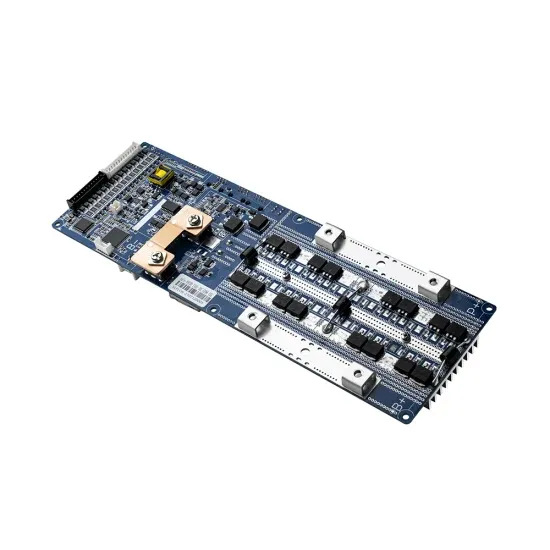

Elimination of circulating current in parallel operation of
Apr 1, 2022 · This paper presents the control strategy for parallel operation of an inverter to eliminate DC & AC circulating current. This paper also analyses the cross-current between

Design and implementation of a virtual capacitor based DC current
Sep 1, 2019 · To solve these problems, this paper proposes a virtual-capacitor based DC current suppression control technique for grid-connected inverters, which has the advantages of fast

An intelligent dc current minimization method for
May 1, 2019 · In [18], the dc current injection suppression to the grid for a three-phase inverter is realized by accurately sensing the dc component of line voltages of three-phase inverter and

What is an On Grid Solar Inverter? Definition, Components,
Jan 19, 2025 · An on grid solar inverter is a key component in solar power systems that are connected to the main power grid. Its primary function is to convert the direct current (DC)
6 FAQs about [Inverter DC current component]
What are the components of a DC inverter?
DC Input: This is where the inverter connects to the DC power source. The power source could be solar panels, batteries, or other DC supplies. This component ensures that the inverter can receive electrical energy from these sources. Rectifier: In some inverters, a rectifier is essential, especially for converting AC to DC.
What is a DC inverter?
An inverter is an electrical device or circuit that converts direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC). Inverters are essential in various applications, enabling the use of DC power sources, such as batteries or solar panels, to operate AC-powered devices and systems. Following is the basic configuration of inverter.
What is a DC input in an inverter?
The DC input is responsible for providing a steady and consistent flow of energy, which the inverter will later convert into AC power. This component is vital in ensuring energy availability for the inverter’s operation. The power electronics circuit is a core component of an inverter.
What is a DC input in a solar inverter?
The DC input is the power input for solar panels or batteries. Poor quality terminals or improper surge protection can cause power fluctuations or even system failure. It consists of the following two parts: Fuse: The fuse automatically opens if the current is too high, protecting the inverter from damage.
What is an inverter circuit?
An inverter circuit is an electrical circuit that converts DC current into AC current to power appliances and devices in everyday life. Inverter circuits have experienced rapid development, especially in the last two decades, along with the increasing use of solar power systems as a clean, renewable energy source.
What is the basic configuration of an inverter?
Following is the basic configuration of inverter. An inverter typically consists of several key components, each serving a specific function in the process of converting direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC) with variable frequency. What is Inverter?
Random Links
- Portable ACDC Power Supply
- Damascus industrial-grade UPS uninterruptible power supply
- Which manufacturer of outdoor communication battery cabinets in South America should I look for
- Mexico 5g communication green base station equipment cabinet manufacturer
- Advantages of Macedonia s corrosion-resistant photovoltaic curtain wall
- Abuja Industrial and Commercial Energy Storage Cabinet Customization Company
- Good photovoltaic panel manufacturers
- Flywheel energy storage flies out
- Flywheel energy storage data
- Technological innovation in new energy storage
- Prospects for energy storage development in Grenada Industrial Park
- Distribution breaker in China in Netherlands
- Copenhagen makes energy storage batteries
- Communication base station inverter grid-connected installation power supply
- Container Generator Selection
- Single phase breaker for sale in Ireland
- Five 400 watt solar power generation
- Polish communication base station flow battery tower
- What is the use of stacked energy storage power supply
- Solar panels for buoy system
- Off-grid photovoltaic energy storage cabinet
- Hot sale China camping charger station Wholesaler
- Communication base station EMS is crowded
Residential Solar Storage & Inverter Market Growth
The global residential solar storage and inverter market is experiencing rapid expansion, with demand increasing by over 300% in the past three years. Home energy storage solutions now account for approximately 35% of all new residential solar installations worldwide. North America leads with 38% market share, driven by homeowner energy independence goals and federal tax credits that reduce total system costs by 26-30%. Europe follows with 32% market share, where standardized home storage designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting residential storage for backup power and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 4-7 years. Modern home installations now feature integrated systems with 10-30kWh capacity at costs below $700/kWh for complete residential energy solutions.
Home Solar System Innovations & Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving home solar storage and inverter performance while reducing costs. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 40% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 15+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,200/kW to $650/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow home systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing homeowner savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for solar storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $600/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have improved ROI significantly, with residential projects typically achieving payback in 5-8 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard home systems (5-10kWh) starting at $8,000 and premium systems (15-20kWh) from $12,000, with financing options available for homeowners.
