
Solar Panels Series vs Parallel:Understanding and Difference
Dec 1, 2023 · For a quick explanation, the main difference between solar panels connected in series and parallel is the output voltage and output current. The output voltage of a series

Performance study of a combined low-concentration bifacial photovoltaic
Jun 1, 2021 · The combination of photovoltaic and photothermal, often abbreviated as PV/T, is a promising approach that has been increasingly studied to improve solar energy conversion

Chapter Number 3.0 Solar PV modules Explained in detail
Mar 29, 2023 · A solar PV module is a collection of solar cells, mainly connected in series. These combinations of Solar Cell provide higher power than a single solar cell. The PV modules are
Module configurations in photovoltaic system: A review
Jan 1, 2017 · 3. Conclusion This paper discussed the basic concept of PV module configuration. It also highlights the findings of researchers on different configurations like series, parallel, series

6 FAQs about [Photovoltaic glass in parallel or in series]
What is the difference between series and parallel solar panels?
Understanding the differences between solar panels in series vs parallel connections is vital for designing a solar system that maximizes performance and longevity. Series wiring increases voltage and suits high-voltage applications but is more affected by shading.
What is a solar panel series parallel connection?
Solar panel series-parallel connection is a method of linking solar panels together to meet specific current and voltage requirements, in order to more efficiently harness solar energy and convert it into electricity. Previous Post : What are the advantages of a Commercial Solar System? Next Post : N-Type Solar Panels VS. P-Type Solar Panels
Should photovoltaic panels be connected in series or parallel?
Connecting photovoltaic panels with different power is not recommended, either in series or parallel. This is because, in both types of joints, the modules with the worst parameters will affect the efficiency of the remaining ones, ultimately reducing the efficiency of the entire installation.
How to connect photovoltaic panels in series?
Connecting photovoltaic panels in series involves connecting their cables according to the pluses and minuses principle. This connection causes the voltage in each circuit to increase while the current in a single string remains the same as in one module. This type of connection was widely used.
What is the difference between a series and parallel connection?
When setting up a solar power system, understanding the differences between series and parallel connections is crucial. These two configurations impact how voltage and current behave within the system. In a series connection, solar panels are linked end-to-end, where the positive terminal of one panel connects to the negative terminal of the next.
What is the difference between parallel wiring and a solar panel?
The right answer depends on the number of PV modules, the planned layout, and your electricity generation goals. So, what’s the difference? Parallel wiring increases the sum output amperage of a solar panel array while keeping the voltage the same. The choice you make can have a significant impact on your system’s overall performance.
Random Links
- Rwanda PV DC combiner box installation
- Photovoltaic glass softening temperature
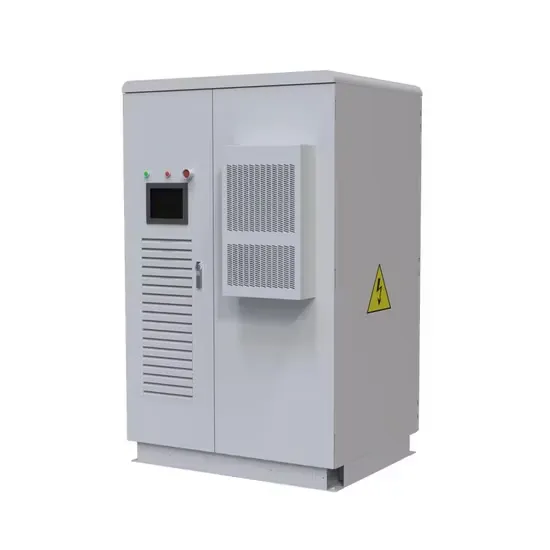
- Ireland 72v battery cabinet
- Solar Street Light Inverter
- Uninterruptible power supply room of Kigali communication base station
- How big a battery does a 60 watt solar panel correspond to
- Hybrid inverter mppt in China in Germany
- Ashgabat solar water pump
- Montevideo photovoltaic panel price per square meter
- Outdoor power supply discharge time
- Factory price 225 amp breaker in Cameroon
- Container energy storage fire protection system
- Koten circuit breaker factory in Korea
- Pakistan Energy Storage Project
- Portable Electricity Storage Prices in Ghana
- Batch customization of Thimphu energy storage batteries
- How much does solar energy storage power cost in Yemen
- Is the EPS host a battery cabinet
- High quality wholesale 100ah power station Factory
- High quality 1 2 kva inverter in Guatemala
- High quality wholesale 4000 amp switchgear Seller
- Solar Cycle System Services
- Inverter requires output voltage
Residential Solar Storage & Inverter Market Growth
The global residential solar storage and inverter market is experiencing rapid expansion, with demand increasing by over 300% in the past three years. Home energy storage solutions now account for approximately 35% of all new residential solar installations worldwide. North America leads with 38% market share, driven by homeowner energy independence goals and federal tax credits that reduce total system costs by 26-30%. Europe follows with 32% market share, where standardized home storage designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting residential storage for backup power and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 4-7 years. Modern home installations now feature integrated systems with 10-30kWh capacity at costs below $700/kWh for complete residential energy solutions.
Home Solar System Innovations & Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving home solar storage and inverter performance while reducing costs. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 40% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 15+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,200/kW to $650/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow home systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing homeowner savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for solar storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $600/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have improved ROI significantly, with residential projects typically achieving payback in 5-8 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard home systems (5-10kWh) starting at $8,000 and premium systems (15-20kWh) from $12,000, with financing options available for homeowners.
