
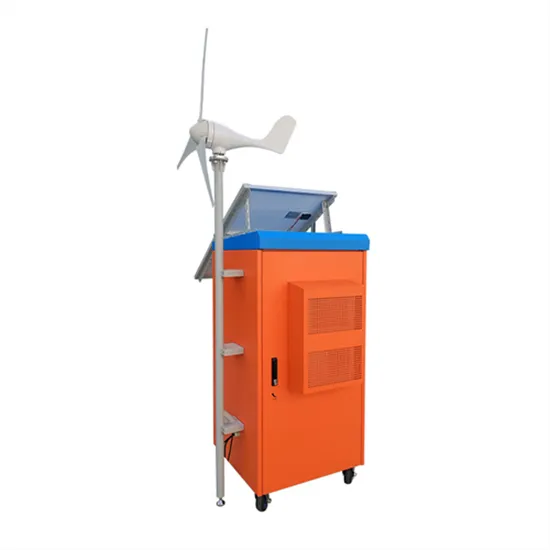
Design of 3KW Wind and Solar Hybrid Independent Power Supply System for
Nov 30, 2009 · This paper studies structure design and control system of 3 KW wind and solar hybrid power systems for 3G base station. The system merges into 3G base stations to save

A review of hybrid renewable energy systems: Solar and wind
Dec 1, 2023 · However, such systems mitigate the intermittency issues inherent to individual renewable sources, enhancing the overall reliability and stability of energy generation. Solar
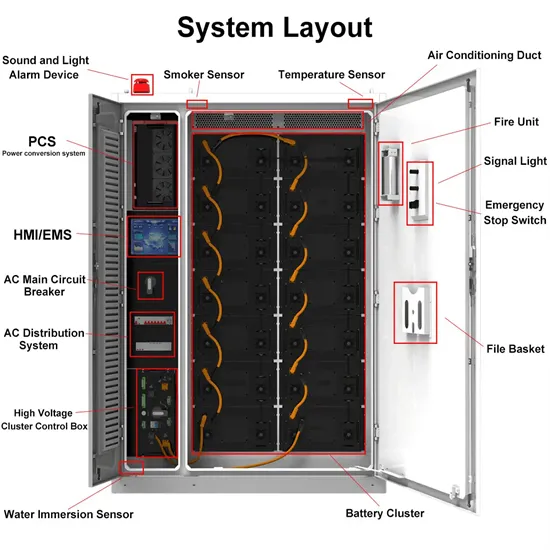
Control System of 3KW Wind Power Independent Power Supply for 3G Base
Nov 30, 2009 · The system merges into 3G base stations to save power in order to fully ensure that base stations can get supply power normally in any case. The outputs of the system
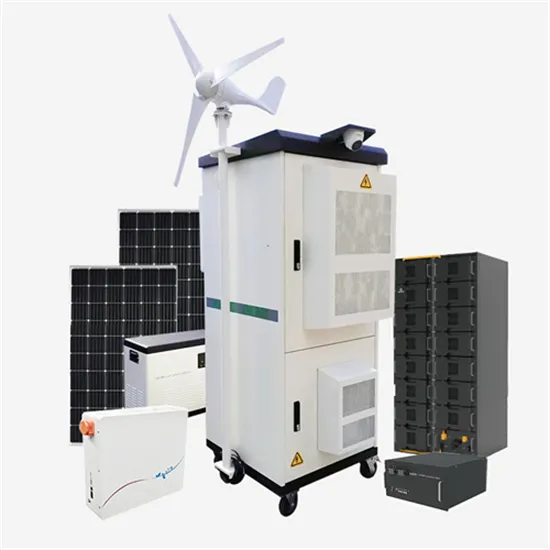

Design of 3KW Wind and Solar Hybrid Independent Power Supply System for
Jan 1, 2010 · This paper studies structure design and control system of 3 KW wind and solar hybrid power systems for 3G base station. The system merges into 3G base stations to save

Control System of 3KW Wind Power Independent Power Supply for 3G Base
Nov 30, 2009 · This paper studies control system operation and control strategy of 3 KW wind power generation for 3G base station. The system merges into 3G base stations to save

6 FAQs about [What does the base station wind power supply consist of ]
How do wind power stations work?
A wind power station, often known as a wind farm, captures wind’s kinetic energy and turns it into electricity. Here’s an explanation of how do wind power stations work internally: 1. Wind Turbines: Wind turbines are the principal component of a wind power facility. They consist of enormous blades attached to a hub installed on top of a tall tower.
What are the components of a wind power facility?
1. Wind Turbines: Wind turbines are the principal component of a wind power facility. They consist of enormous blades attached to a hub installed on top of a tall tower. Wind speeds rise with altitude, so the height of the tower is significant. 2. Wind Capture: As the wind blows, turbine blades rotate.
What are the components of a wind turbine?
A wind turbine consists of five main parts and many smaller parts. The main components are the foundation, the tower, the rotor and hub (including three blades), the nacelle, and the generator. The installation of all these elements requires specific wind turbine equipment to meet the needs of each one. 1. Wind turbine foundation
How does a wind turbine nacelle work?
The nacelle of a wind turbine is a complex electromechanical system with quite a few components that function correctly with precision. Significant turbine parts are the generator and the turbine shaft which transfers the energy from the wind to the generator through a gearbox.
Why do wind turbines have three sections?
Towers usually come in three sections and are assembled on-site. Because wind speed increases with height, taller towers enable turbines to capture more energy and generate more electricity. Winds at elevations of 30 meters (roughly 100 feet) or higher are also less turbulent. Determines the design of the turbine.
What are the components of a horizontal axis wind turbine?
To summarize, the main components constituting horizontal axis wind turbines are: The converter and the transformer can be installed directly in the nacelle as Figure 1 shows, or positioned at the base of the tower.
Random Links
- Battery cabinet base station power system introduction
- Flywheel energy storage project cost
- Photovoltaic energy storage in rural areas of the Middle East
- Energy storage product production in Tanzania
- Boston Uninterruptible Power Supply Manufacturer
- Libreville Energy Storage Container BESS
- How to connect rooftop photovoltaic containers to solar energy
- Replacing a breaker for sale in Dominican-Republic
- St George Solar Photovoltaic Power Supply System
- Kampala Outdoor Power Company
- Guinea-Bissau inverter manufacturer
- Which energy storage photovoltaic power generation company in Mexico is the best
- Vanuatu Electricity Authority Base Station
- How many energy storage power stations are there in Nicosia
- Power breaker switch factory in Monaco
- Honiara Personal Inverter Manufacturer Quote
- Base station conversion outdoor power supply
- Lithium battery pack for solar energy
- High quality solar power unit in Brisbane
- RV 30 kW solar power generation
- Agricultural users outdoor high-power energy storage power supply
- San Jose Energy Storage System Classification
- Photovoltaic 1mw energy storage
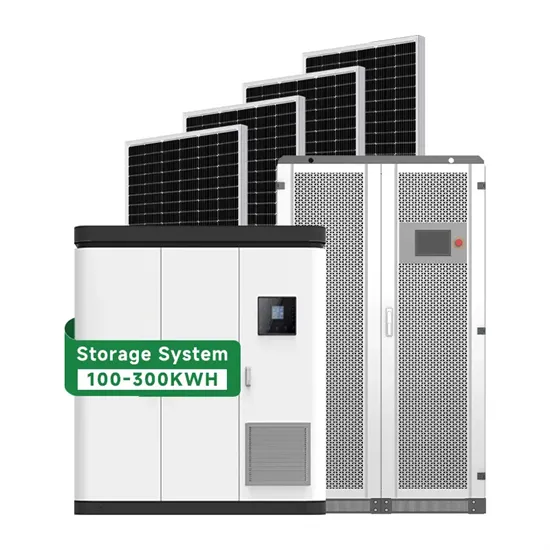
Residential Solar Storage & Inverter Market Growth
The global residential solar storage and inverter market is experiencing rapid expansion, with demand increasing by over 300% in the past three years. Home energy storage solutions now account for approximately 35% of all new residential solar installations worldwide. North America leads with 38% market share, driven by homeowner energy independence goals and federal tax credits that reduce total system costs by 26-30%. Europe follows with 32% market share, where standardized home storage designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting residential storage for backup power and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 4-7 years. Modern home installations now feature integrated systems with 10-30kWh capacity at costs below $700/kWh for complete residential energy solutions.
Home Solar System Innovations & Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving home solar storage and inverter performance while reducing costs. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 40% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 15+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,200/kW to $650/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow home systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing homeowner savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for solar storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $600/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have improved ROI significantly, with residential projects typically achieving payback in 5-8 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard home systems (5-10kWh) starting at $8,000 and premium systems (15-20kWh) from $12,000, with financing options available for homeowners.
