
Power Inverters for Home: Essential Guide to Reliable Energy
Jul 14, 2025 · Power inverters for home are the silent guardians of modern energy resilience, transforming the way we think about backup power and sustainability. At their core, a power
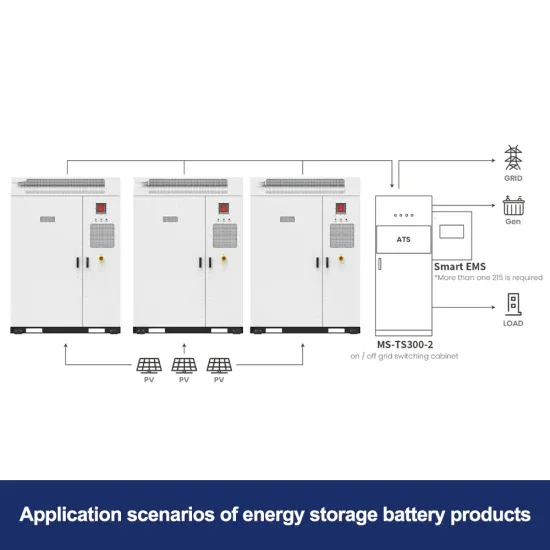
6 FAQs about [Household electricity and inverter are different]
What is the difference between inverter and converter?
Difference between inverter and converter? An inverter changes DC power to AC power, while a converter does the opposite, turning AC power into DC. Inverters are used for solar systems, while converters are more common in electrical devices.
What is the difference between AC and DC power inverters?
In contrast, inverters are specifically designed to convert DC power into AC power, making it suitable for use with household appliances and electrical grids. This conversion is crucial because most devices and infrastructure operate on AC power, while many power sources, like solar panels and batteries, produce DC power.
What is an inverter & how does it work?
An inverter is a device that converts direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC), enabling the use of DC power sources, such as batteries or solar panels, to power AC appliances.
When should I use an inverter?
Use an Inverter When: You need to convert DC to AC (e.g., solar power systems, backup generators). You’re powering sensitive electronics that require a clean and stable AC power source. You’re running an electric vehicle and need to convert battery power (DC) into AC for the motor. Use a Converter When:
Does an inverter have in-built energy storage?
However, in inverters, there is no option for in-built energy storage, the battery is externally located and the inverter derives power from the battery when required. UPS provides a backup power supply for appliances, particularly computers so that they keep on functioning properly for a few minutes during a power outage.
What are inverters used for?
Inverters: Commonly used in renewable energy systems (such as solar power), uninterruptible power supplies, and electric vehicles. Converters: Used in power supply units, battery charging systems, and voltage regulation for devices requiring different voltage levels. Energy Transformation Inverters: Mainly transform energy from DC to AC.
Random Links
- Jerusalem High Frequency Inverter
- 3000 watts of solar panels
- Huawei Thailand portable photovoltaic panels
- Photovoltaic power station cooperates with 5g base station
- Cuba Energy Storage Project Investment
- Bandar Seri Begawan portable photovoltaic panel price
- Helsinki Power Storage Vehicle Customization Company
- Naypyidaw Solar Air Conditioning
- Chilean Liquid Flow Battery
- Inverter changes voltage to 220V
- Photovoltaic grid synchronous inverter
- Uruguay backup power storage development prospects
- 48v80ah lead acid battery inverter
- Battery cabinet automatic feeding device
- Advantages and disadvantages of one-to-four micro inverters
- Rabat personal inverter custom price
- Paramaribo export energy storage container manufacturer
- Huawei Maseru Energy Storage Project Franchise Conditions
- 3 7 to 220V inverter
- Kosovo Industrial and Commercial Grid-side Energy Storage Solution
- RV Batteries and Inverters
- Can three inverters be connected in parallel to form three-phase electricity
- Lithium battery BMS safety standards
Residential Solar Storage & Inverter Market Growth
The global residential solar storage and inverter market is experiencing rapid expansion, with demand increasing by over 300% in the past three years. Home energy storage solutions now account for approximately 35% of all new residential solar installations worldwide. North America leads with 38% market share, driven by homeowner energy independence goals and federal tax credits that reduce total system costs by 26-30%. Europe follows with 32% market share, where standardized home storage designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting residential storage for backup power and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 4-7 years. Modern home installations now feature integrated systems with 10-30kWh capacity at costs below $700/kWh for complete residential energy solutions.
Home Solar System Innovations & Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving home solar storage and inverter performance while reducing costs. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 40% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 15+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,200/kW to $650/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow home systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing homeowner savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for solar storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $600/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have improved ROI significantly, with residential projects typically achieving payback in 5-8 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard home systems (5-10kWh) starting at $8,000 and premium systems (15-20kWh) from $12,000, with financing options available for homeowners.
