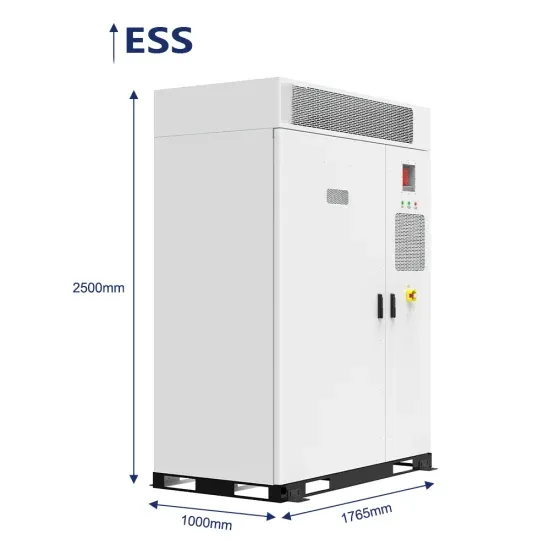

Understanding Frequency Inverters: A Comprehensive Guide
Feb 23, 2025 · Low-Frequency Inverter: An Overview A low-frequency inverter operates at a lower switching frequency, typically below 60 Hz. It is designed for applications requiring high power
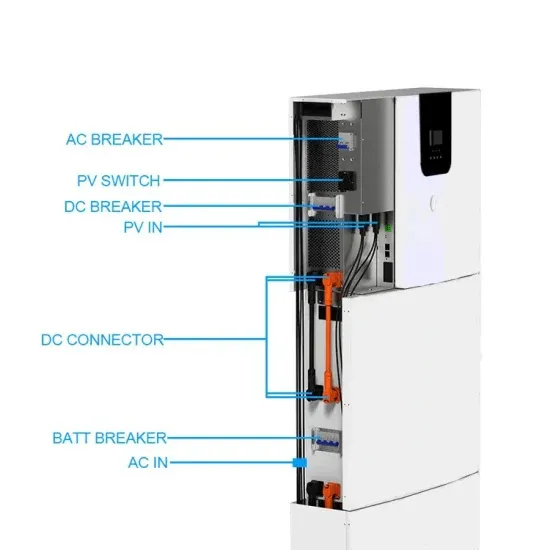
Low vs High frequency inverters | DIY Solar Power Forum
Jun 13, 2022 · Small high frequency ferrite core transformers saturate quickly giving little time for any overload detection circuitry to react and shutdown inverter to save MOSFET drivers. Also
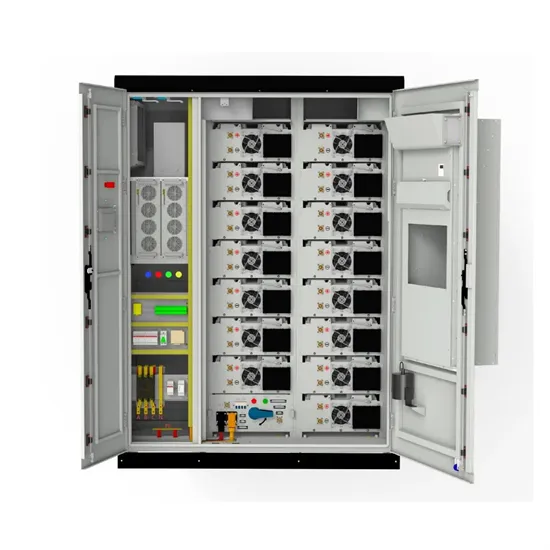

High Frequency Power Inverters: A Guide To Modern Solutions
May 4, 2024 · Welcome to our comprehensive guide on high frequency power inverters! In an era driven by innovation and energy-efficient technologies, power inverters play a crucial role in

Complete Comparison: High Frequency vs Low Frequency Inverters
May 7, 2025 · High-frequency inverters: Best for urban homes, offices, and grid-connected solar systems. Low-frequency inverters: Perfect for villages, agriculture, and industrial machinery.

Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Best Frequency Inverter for
Jun 14, 2025 · This ultimate guide will explore the industry standards associated with frequency inverters, highlight common problems encountered during selection, and offer insights into
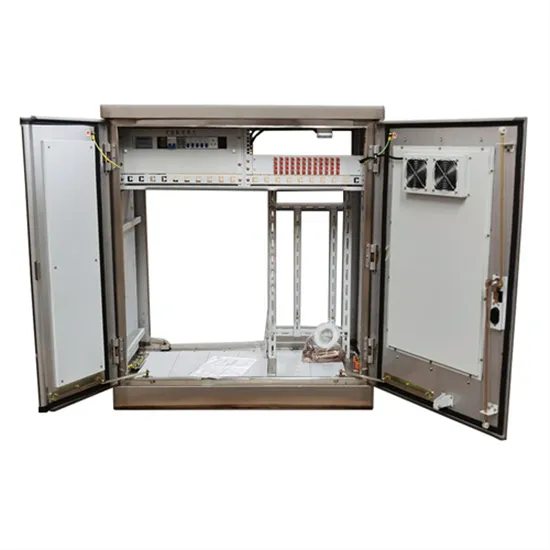

Top Solar inverter Manufacturers Suppliers in Azerbaijan
Jul 28, 2025 · Solar inverters convert the direct current (DC) output of panels to the alternating current (AC) on which most residential and commercial appliances run. In short, the inverters

6 FAQs about [Which is the best high frequency inverter in Azerbaijan]
Which inverter is best?
The best inverter is the low-frequency inverter. This is because it can handle more surge power and is more reliable. A high-frequency inverter will be good enough if you have pure resistive loads like lights and electronics. Interested in finding out the best inverter? Read my expert article here. Conclusion
What is a low frequency inverter?
Efficiency: Low-frequency inverters are known for their robustness and ability to handle high surge currents, making them suitable for powering heavy-duty appliances or equipment with high starting currents, such as motors and compressors.
Are high-frequency inverters better than low-frequency?
Weight: High-frequency inverters are lighter than low-frequency inverters, using smaller, lighter transformers. Efficiency: High-frequency inverters are generally more efficient than low-frequency inverters for maintaining a constant load for lighter loads. However, they may struggle with high surge currents or heavy loads.
What is a high frequency inverter?
Applications: These inverters are more suitable for off-grid systems where heavy loads and extreme conditions are expected, such as in industrial applications or in remote locations with harsh environments. Weight: High-frequency inverters are lighter than low-frequency inverters, using smaller, lighter transformers.
Are low frequency inverters reliable?
These transformers operate at lower frequencies (typically 50 or 60 Hz), making them robust and highly reliable. Low-frequency inverters are known for their durability and ability to handle high surge loads.
Does victron use a high frequency inverter?
Victron combines both inverters, which they call Hybrid HF or Combined high frequency and line frequency technologies. What frequency inverter does growatt use? Growatt uses a high-frequency inverter. Which one is best? Low or high frequency? The best inverter is the low-frequency inverter.
Random Links
- Baghdad Distributed Energy Storage
- Solar energy storage integrated power generation system
- Wind power generation system base
- Niamey photovoltaic panels wholesale factory direct sales
- Beijing Energy Storage Pumped Photovoltaic Power Station Project Owner
- Energy Storage Equipment 2025
- Outdoor power supply at 300 yuan per kilowatt-hour
- Energy storage cabinet strong light battery
- Air-cooled battery energy storage box
- Three-phase solar power inverter
- Monrovia Street New Energy Line Station
- Huawei s latest photovoltaic inverter
- High quality 240 volt breaker in Nicaragua
- How long does it take to charge the battery cabinet at high power
- Nicosia shingled solar panel manufacturer
- Cheap wholesale smes energy storage Wholesaler
- Andorra outdoor communication battery cabinet supplier
- High frequency 80kw inverter
- Advantages and disadvantages of two-wheel energy storage lithium batteries
- North America Photovoltaic Folding Container Size Wholesale
- Capacitor Energy Storage Prices in the Middle East
- Source-grid-load-storage-electrochemical energy storage
- Danish high power ups uninterruptible power supply price
Residential Solar Storage & Inverter Market Growth
The global residential solar storage and inverter market is experiencing rapid expansion, with demand increasing by over 300% in the past three years. Home energy storage solutions now account for approximately 35% of all new residential solar installations worldwide. North America leads with 38% market share, driven by homeowner energy independence goals and federal tax credits that reduce total system costs by 26-30%. Europe follows with 32% market share, where standardized home storage designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting residential storage for backup power and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 4-7 years. Modern home installations now feature integrated systems with 10-30kWh capacity at costs below $700/kWh for complete residential energy solutions.
Home Solar System Innovations & Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving home solar storage and inverter performance while reducing costs. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 40% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 15+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,200/kW to $650/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow home systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing homeowner savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for solar storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $600/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have improved ROI significantly, with residential projects typically achieving payback in 5-8 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard home systems (5-10kWh) starting at $8,000 and premium systems (15-20kWh) from $12,000, with financing options available for homeowners.
