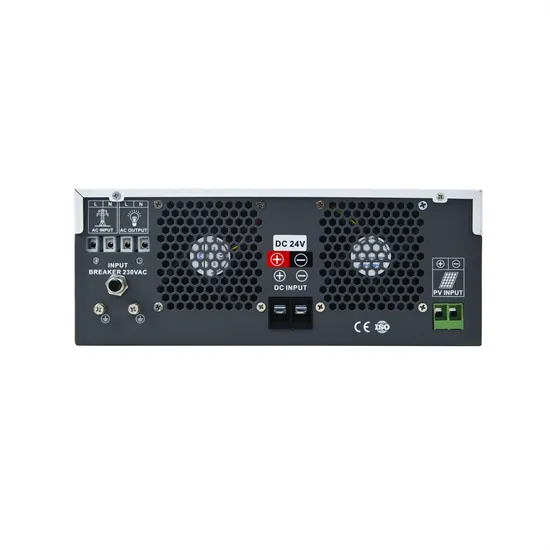

Hybrid compatible grid forming inverters with coordinated
Aug 16, 2025 · This guarantees that the inverter maintains stable operation in both grid-connected and islanded modes, effectively supporting frequency regulation, voltage control, and power
Multiple-Objective Control Scheme for Input-Series–Output-Series
Jan 6, 2020 · An input-series-output-series inverter system is suitable for the large-capacity high-voltage ac power applications. If such a combined system comprising a number of small

Control Scheme to Achieve Multiple Objectives and
Feb 13, 2019 · Input-series-output-parallel (ISOP) inverter system is very suitable for high dc input voltage and large ac output current power conversion applications. If this topology is applied to

A comprehensive review on inverter topologies and control strategies
Oct 1, 2018 · The requirements for the grid-connected inverter include; low total harmonic distortion of the currents injected into the grid, maximum power point tracking, high efficiency,

Grid-connected Micro-inverter Installation and User
May 1, 2023 · 1. Important safety information This manual contains important instructions to follow during installation and maintenance of the APS Photovoltaic Grid-connected Micro-inverter. To
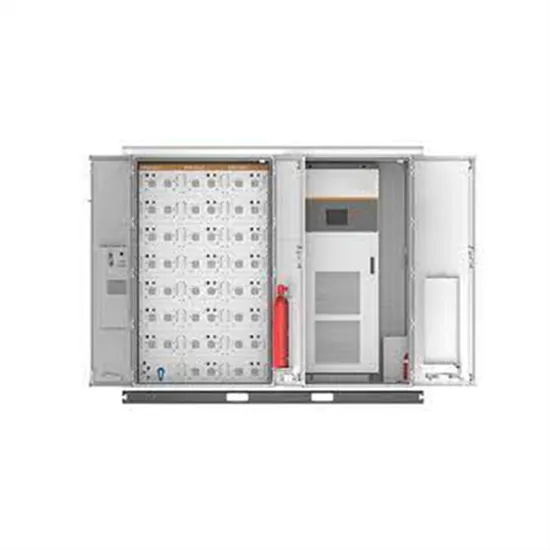

Design of series submodular photovoltaic grid-connected inverter
Sep 22, 2024 · The grid-connected algorithm and the sub-module capacitor voltage sharing algorithm for this topology are proposed. The control of the grid-connected algorithm is very

Series Resonant Current Source High-frequency Link Inverter Grid
Nov 11, 2024 · This paper proposes a novel series resonant grid-connected high-frequency link inverter, which can achieve DC-AC conversion and bidirectional energy flow in a single stage.
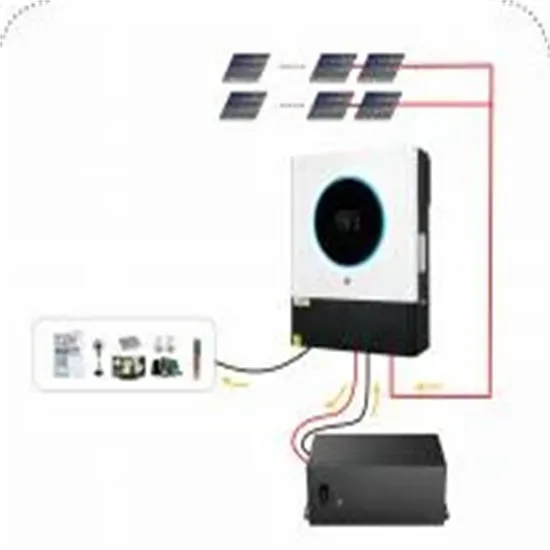

Design of series submodular photovoltaic grid-connected inverter
Sep 22, 2024 · In order to verify the feasibility of the method, this paper uses the simulation platform to build a grid-connected PV inverter model with 7-stage series sub-modules. The

Overview of technical specifications for grid-connected
Nov 15, 2017 · In [8] standards and specifications of grid-connected PV inverter, grid-connected PV inverter topologies, Transformers and types of interconnections, multilevel inverters, soft

Solar PV-Fed Multilevel Inverter With Series Compensator for
Aug 3, 2022 · Power quality difficulties arise as a result of Renewable Energy Sources (RES) integrating with the grid. Voltage swell, sag, and harmonic distortion occur on the grid due to
6 FAQs about [Series grid-connected inverter]
How are multiple inverters connected to a grid?
Then multiple inverters are connected to the grid through the Point of Common Coupling (PCC) point. The modal analysis method is applied to identify its existing resonance frequency. Figure 3 shows the topology of a single-phase LCL grid-connected inverter.
What is the difference between grid connected current and inverter?
The grid-connected current has a stronger ability to suppress the background harmonics of grid voltage, while the inverter has better grid-connected performance.
What is a grid-connected inverter?
In the grid-connected inverter, the associated well-known variations can be classified in the unknown changing loads, distribution network uncertainties, and variations on the demanded reactive and active powers of the connected grid.
What is a series connected PV inverter?
Compared to the parallel-connected inverter structure, the output voltage of each inverter in the series-connected structure is superimposed, which enables the cluster of low-voltage PV inverters to be directly connected into the medium-high voltage power network without the need for a step-up transformer.
Is there a decentralized control strategy for series-connected PV inverters?
7. Conclusions In this paper, a decentralized control strategy for series-connected single-phase two-stage grid-connected PV inverters is proposed, which only requires local information to achieve a consistent phase and frequency of the output voltage of each unit and self-synchronization with the power grid.
Can grid-connected PV inverters improve utility grid stability?
Grid-connected PV inverters have traditionally been thought as active power sources with an emphasis on maximizing power extraction from the PV modules. While maximizing power transfer remains a top priority, utility grid stability is now widely acknowledged to benefit from several auxiliary services that grid-connected PV inverters may offer.
Random Links
- Heyi New Energy Lithium Battery Cylindrical
- Generator switchgear in China in Brisbane
- How much is a 540w solar photovoltaic panel per megawatt
- Factory price voltage breaker in Albania
- Maldives RV modified lithium battery pack
- Kuala Lumpur Photovoltaic Panel Solar Street Light Factory
- Apia Energy Storage Container Quote
- Windhoek portable power bank sw6117
- Original ore of photovoltaic glass
- Maseru Photovoltaic Combiner Box
- Tripoli imported energy storage battery company
- HJ Solar Wall Mounted Container Price
- Lithium battery factory 1MWH container base station
- Outdoor communication power supply BESS source
- Factory price furnace breaker in Tunisia
- Vatican Energy Storage Photovoltaic Box Substation Model
- How much electricity can the energy storage cabinet save
- Mobile outdoor power cooperation
- Nouakchott home uninterruptible power supply equipment
- Kathmandu villa solar air conditioning
- Sine wave inverter full load
- Photovoltaic panels power generation in farms
- 50 cylindrical lithium battery
Residential Solar Storage & Inverter Market Growth
The global residential solar storage and inverter market is experiencing rapid expansion, with demand increasing by over 300% in the past three years. Home energy storage solutions now account for approximately 35% of all new residential solar installations worldwide. North America leads with 38% market share, driven by homeowner energy independence goals and federal tax credits that reduce total system costs by 26-30%. Europe follows with 32% market share, where standardized home storage designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting residential storage for backup power and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 4-7 years. Modern home installations now feature integrated systems with 10-30kWh capacity at costs below $700/kWh for complete residential energy solutions.
Home Solar System Innovations & Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving home solar storage and inverter performance while reducing costs. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 40% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 15+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,200/kW to $650/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow home systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing homeowner savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for solar storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $600/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have improved ROI significantly, with residential projects typically achieving payback in 5-8 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard home systems (5-10kWh) starting at $8,000 and premium systems (15-20kWh) from $12,000, with financing options available for homeowners.
