
Implementation of a Solar-Wind hybrid Charging Station For
Jul 20, 2023 · This work focuses on a grid-connected solar-wind hybrid system with a charging station for electric vehicles. The charging system is powered by a combination of solar, wind,
(PDF) Hybrid Off-Grid SPV/WTG Power System for Remote Cellular Base
Dec 23, 2016 · Accordingly, this study examined the feasibility of using a hybrid solar photovoltaic (SPV)/wind turbine generator (WTG) system to feed the remote Long Term Evolution-macro

Solution of Mobile Base Station Based on Hybrid System of Wind
Mar 14, 2022 · The development of renewable energy provides a new choice for power supply of communication base stations. This paper designs a wind, solar, energy storage, hydrogen

Hybrid renewable power systems for mobile telephony base stations
Mar 1, 2013 · This paper investigates the possibility of using hybrid Photovoltaic–Wind renewable systems as primary sources of energy to supply mobile telephone Base Transceiver Stations

Assessing the impact of climate change on the optimal solar–wind hybrid
Apr 1, 2025 · To mitigate the impact of climate change, an increasing number of countries have committed to transforming their energy systems into zero – emissions systems. Decarbonizing

A review of hybrid renewable energy systems: Solar and wind
Dec 1, 2023 · This hybrid system can take advantage of the complementary nature of solar and wind energy: solar panels produce more electricity during sunny days when the wind might not

Wind Solar Hybrid Power System for the Communication Base
Apr 27, 2020 · There are still many places without electricity in Xinjiang, especially the borders, grasslands and deserts. For mobile companies, the electrical load in those remote areas is

Integrating solar and wind energy into the electricity grid for
Jan 1, 2025 · A rise in the need for the integration of renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar power, has been attributed to the search for sustainable energy solutions. To strengthen

Techno-economic assessment of solar PV/fuel cell hybrid
May 27, 2023 · This study investigates the viability of deploying solar PV/fuel cell hybrid system to power telecom base stations in Ghana. Furthermore, the study tests the proposed power

Comparative assessment of solar photovoltaic-wind hybrid energy systems
Dec 1, 2021 · Pascasio et al. also used HOMER Pro® software to simulate solar PV-wind systems and determined that small wind turbines are feasible in 139 out of 143 island grids studied
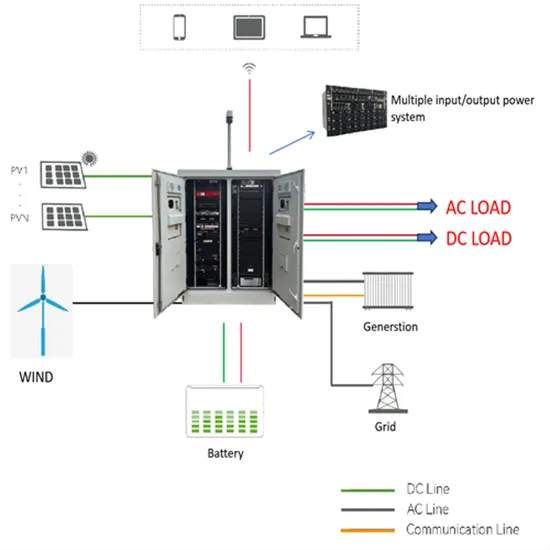

An overview of the policies and models of integrated
Jun 1, 2023 · This study is organized as follows: Section 2 describes the development status of wind and solar generation in China. Section 3 provides the policies of integrated development

6 FAQs about [Foreign countries have communication base stations with wind and solar hybrid outdoor]
Are solar powered cellular base stations a viable solution?
Cellular base stations powered by renewable energy sources such as solar power have emerged as one of the promising solutions to these issues. This article presents an overview of the state-of-the-art in the design and deployment of solar powered cellular base stations.
Are solar powered base stations a good idea?
Base stations that are powered by energy harvested from solar radiation not only reduce the carbon footprint of cellular networks, they can also be implemented with lower capital cost as compared to those using grid or conventional sources of energy . There is a second factor driving the interest in solar powered base stations.
Should solar and wind energy systems be integrated?
Despite the individual merits of solar and wind energy systems, their intermittent nature and geographical limitations have spurred interest in hybrid solutions that maximize efficiency and reliability through integrated systems.
Why are hybrid energy systems more expensive than single-source systems?
Hybrid systems may have higher initial investment costs compared to single-source systems. The variability of renewable energy can affect the predictability of returns on investment. Some technologies in HRES might not be mature, leading to economic uncertainties.
Can a stand-alone solar PV-BT system be used for irrigation in isolated regions?
Rezk et al. conduct a performance evaluation and optimal design of a stand-alone solar PV- BT system for irrigation in isolated regions, focusing on a case study in Al Minya, Egypt. The research aims to determine the economic feasibility and efficiency of the system.
How can a hybrid energy system improve grid stability?
By incorporating hybrid systems with energy storage capabilities, these fluctuations can be better managed, and surplus energy can be injected into the grid during peak demand periods. This not only enhances grid stability but also reduces grid congestion, enabling a smoother integration of renewable energy into existing energy infrastructures.
Random Links
- Costa Rica Mobile Power Station Generator Manufacturer
- Taipei Photovoltaic Glass
- Communication 5g signal tower base station energy method
- High quality wholesale c16 circuit breaker producer
- Thailand Hybrid Battery Energy Storage Project
- Azerbaijan energy storage battery sales
- Algeria pure sine wave inverter sales
- Network battery cabinet website
- The current of the photovoltaic combiner box is zero
- City-level grid-side energy storage
- Solar inverters in Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Tashkent solar air conditioning construction site dedicated
- Zagreb energy storage cabinet sales factory operation
- The largest energy storage project in Bergen Norway
- 12v10a power supply portable
- Syria single phase 25kw off-grid inverter
- West Asia Photovoltaic Cell Module
- Huawei power generation panels photovoltaic panels
- Mbabane Wind Power Energy Storage Project
- Huawei foldable photovoltaic panels in Sydney Australia
- Venezuela 5G base station electromagnetic
- Wind power air compression energy storage
- Dubai s home energy storage companies
Residential Solar Storage & Inverter Market Growth
The global residential solar storage and inverter market is experiencing rapid expansion, with demand increasing by over 300% in the past three years. Home energy storage solutions now account for approximately 35% of all new residential solar installations worldwide. North America leads with 38% market share, driven by homeowner energy independence goals and federal tax credits that reduce total system costs by 26-30%. Europe follows with 32% market share, where standardized home storage designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting residential storage for backup power and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 4-7 years. Modern home installations now feature integrated systems with 10-30kWh capacity at costs below $700/kWh for complete residential energy solutions.
Home Solar System Innovations & Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving home solar storage and inverter performance while reducing costs. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 40% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 15+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,200/kW to $650/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow home systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing homeowner savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for solar storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $600/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have improved ROI significantly, with residential projects typically achieving payback in 5-8 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard home systems (5-10kWh) starting at $8,000 and premium systems (15-20kWh) from $12,000, with financing options available for homeowners.
